In this article, we're going to discuss:
- Quick Start: Zendesk Best Practices Checklist
- 1. Foundation: Setting Up Zendesk Correctly
- 2. Ticket Management
- 3. Self-Service Knowledge Base
- 4. Customer Communication
- 5. Analytics, Reporting, and Continuous Improvement
- 6. Health Checks, Change Management, and Disaster Recovery
- 7. Integrations, AI, and Continuous Improvement
- 8. Training, Empowerment, and Support Culture
- Want to optimise your Zendesk with expert help?
Let’s get started with a practical, easy-to-follow Zendesk optimisation checklist.
Quick Start: Zendesk Best Practices Checklist
Before we dive deeper, here’s a practical checklist of Zendesk best practices every support team should consider. Use this checklist to review your current setup or as a template for new Zendesk customisations. These recommendations are based on Zendesk and Premium Plus CX resources:
- Select the most suitable Zendesk plan and add-ons
- Configure user roles and permissions for security
- Customise your Help Centre and improve accessibility
- Optimise ticket forms and fields
- Create macros, smart triggers, and automations
- Define and monitor SLA policies
- Maintain a high-quality knowledge base
- Integrate all key support channels (email, chat, social, voice)
- Set up automated notifications and CSAT surveys
- Build and monitor analytics dashboards
- Schedule regular Zendesk health checks
- Keep a detailed change log
- Onboard and empower your team
- Establish a disaster recovery plan
- Commit to continuous improvement
Ready to put these Zendesk best practices into action? Let’s break down each and show you exactly how to get the best from your Zendesk instance.
Download the free Zendesk Health Check Guide and discover proven tips to:
- boost agent productivity
- optimise triggers and automations
- uncover hidden opportunities in your setup
1. Foundation: Setting Up Zendesk Correctly
Selecting the Right Zendesk Plan and Add-Ons
Choosing the right Zendesk plan and add-ons is the cornerstone of Zendesk best practices. Zendesk offers several tiers: Suite Team, Growth, Professional, and Enterprise. Each is tailored for different business sizes and support needs.
Why it matters:
If you choose a plan that’s too basic, you’ll quickly hit limitations. If you go too big, you’ll pay for features you don’t need. Zendesk experts suggest reviewing your needs every 6–12 months or whenever your business changes significantly.
Benoit Smagghe, Solutions Consultant at Premium Plus, a Zendesk EMEA Partner of the Year
How to do it:
- Assess your needs: Look at your ticket volume, required channels, and reporting needs. For example, a fast-growing e-commerce brand may need multichannel support and advanced Zendesk analytics, while a small local business may do just fine with the basics.
- Review add-ons: Zendesk’s value grows with add-ons like Explore (for analytics), Talk (for phone support), and Guide (for knowledge management).
- Marketplace integrations: The Zendesk Marketplace features hundreds of apps for project management, CRM, translation, and more.
Real-world example:
A SaaS company started on Suite Growth. As their customer base grew, they upgraded to Suite Professional to unlock custom roles, advanced triggers, and reporting. They added Zendesk Chat for real-time support and integrated Salesforce via the Marketplace to connect sales and support.
Pro tip:
Consult Zendesk partners like Premium Plus for health checks and optimisation audits. They’ll help you get the most from your investment.
Configuring Roles and Permissions
One of the most critical Zendesk best practices is controlling who can do what in your Zendesk environment. Proper roles and permissions keep your system secure and your workflows efficient.
Why it matters:
Too many admins can result in accidental misconfiguration or data breaches. Too few permissions can frustrate agents and slow down your support.
How to do it:
- Principle of least privilege: Assign only the permissions an agent needs to perform their role. For example, an agent might need to update tickets but not manage triggers.
- Custom roles: On higher plans, create specific roles like “Knowledge Manager” (can update Help Centre content) or “Junior Agent” (limited to replying and tagging).
- Regular role audits: Schedule quarterly reviews of all user roles. Remove access for staff who have left, and ensure no one has more permissions than necessary.
- Immediate offboarding: Remove access immediately when someone leaves. Don’t wait until your next review.
Example:
A retail team had three admins, 20 agents, and two knowledge managers. After a quarterly audit, they noticed two former staff still had access. They removed those accounts and tightened up their onboarding/offboarding checklist.
2. Ticket Management
Optimising Zendesk Ticket Fields, Forms, and Tags
Good ticket management is a hallmark of Zendesk best practices. The goal is to gather all relevant information from the start so agents spend less time chasing details and more time solving problems.
How to do it:
- Create different ticket forms for different issues (like “Technical Support” or “Billing Inquiry”). Only ask for the information you need for that issue.
- Use dropdowns and checkboxes, not free text, to keep data consistent.
- Auto-tag tickets for reporting and workflow automation.
- Review forms and fields every six months.
Example:
A global wealth management company needed to track every action for compliance. A customised Zendesk solution was tailored to their exact needs. Now, every request starts with a simple, user-friendly form that captures all the right details from the start.
As soon as a ticket is submitted, Zendesk automatically attaches a list of tasks. So nothing important gets missed. Once those tasks are completed, approvals are sent instantly to the right people, keeping everything moving without delay. And, to make sure everything stays secure and efficient, only authorised users have access to these forms and workflows.

Streamlining with Views, Macros, and Triggers
Zendesk best practices for efficiency rely on using views, macros, and triggers to streamline daily work.
Views:
- Shared views: For common queues (e.g., “Unassigned Tickets,” “High Priority”).
- Personal views: For agents to focus on their own work (e.g., “My Pending Tickets”).
Macros:
- Use macros for frequent replies like order tracking info, password reset instructions, or “We’re looking into your issue.”
- Combine macros with actions (add tags, set status, assign group).
Triggers and Automations:
- Assign tickets automatically: Route tickets by topic, channel, or customer type.
- Notifications: Alert agents or managers about urgent issues, SLA breaches, or escalations.
- Automate follow-ups: Use automations to remind agents about pending tickets or to close tickets after a set time with no response.
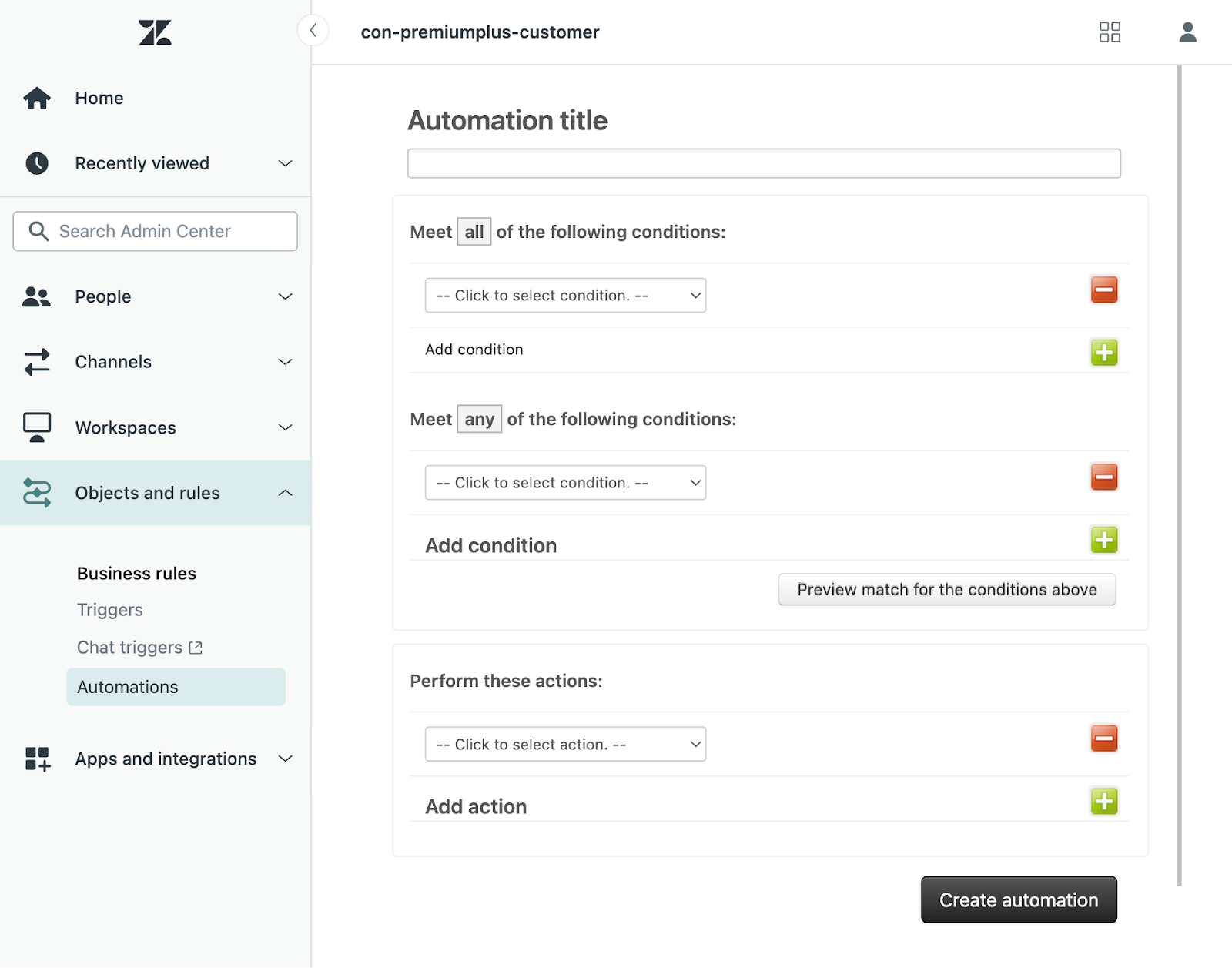
Example:
A retailer uses a macro for “Order Not Received” that adds the “shipping-issue” tag, sets the ticket to “High,” and sends a friendly message to the customer.
Managing SLAs and Prioritisation
SLAs (Service Level Agreements) are your promises to customers. Tracking them is a Zendesk best practice for delivering reliable support.
How to do it:
- Set SLA targets by ticket priority: For example, “Urgent” gets a 1-hour first reply, and “Normal” gets 8 hours.
- Communicate your SLAs clearly: Let customers know what to expect in auto-replies or on your Help Centre.
- Monitor compliance: Use Zendesk Explore to track SLA performance and spot bottlenecks.
- Escalate when needed: Use triggers to flag or escalate tickets in danger of breaching SLAs.
Example:
Jules, a leading fashion retailer in France, supercharged their omnichannel customer experience with improved workflow automations and internal communication. Now their teams can coordinate seamlessly across every channel, making planning and collaboration a breeze. The result? They boosted their SLA achievement to 88%.
Jules, a leading fashion retailer in France, improved their SLA to an
impressive 88%, ensuring faster response times.
3. Self-Service Knowledge Base
Branding and Accessibility
A customised and accessible Zendesk Help Centre is a best practice that pays big dividends in customer trust and satisfaction.
How to do it:
- Custom domain: Use a domain like support.yourbrand.com for a professional touch.
- Brand consistency: Match your company’s colours, logo, and fonts throughout the Help Centre.
- Layout: Customise the layout to highlight FAQs, search bars, or featured articles.
- Accessibility: Use high-contrast colours, readable fonts, and alt text for images. Test your site with accessibility tools to ensure everyone can use it.
Example:
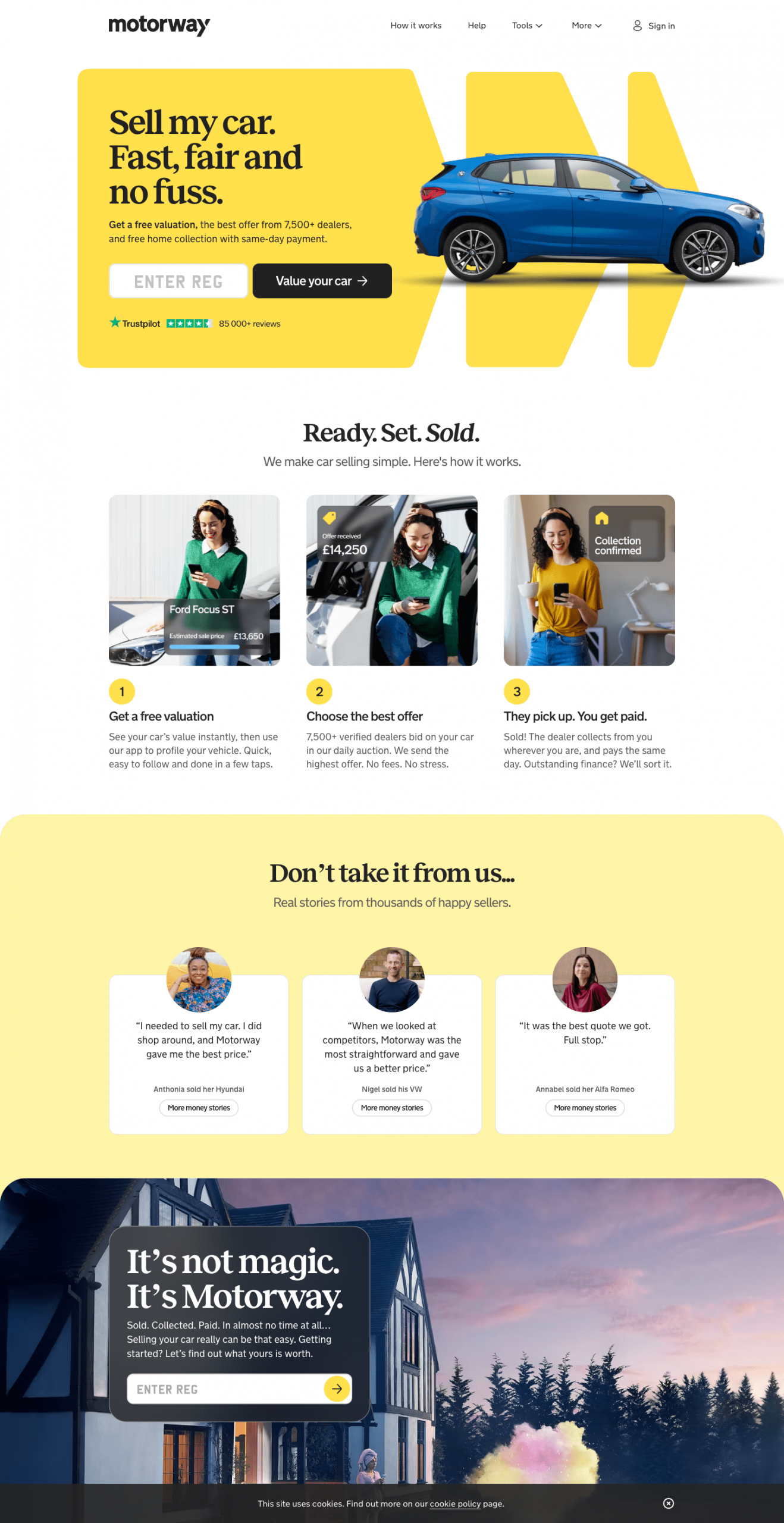
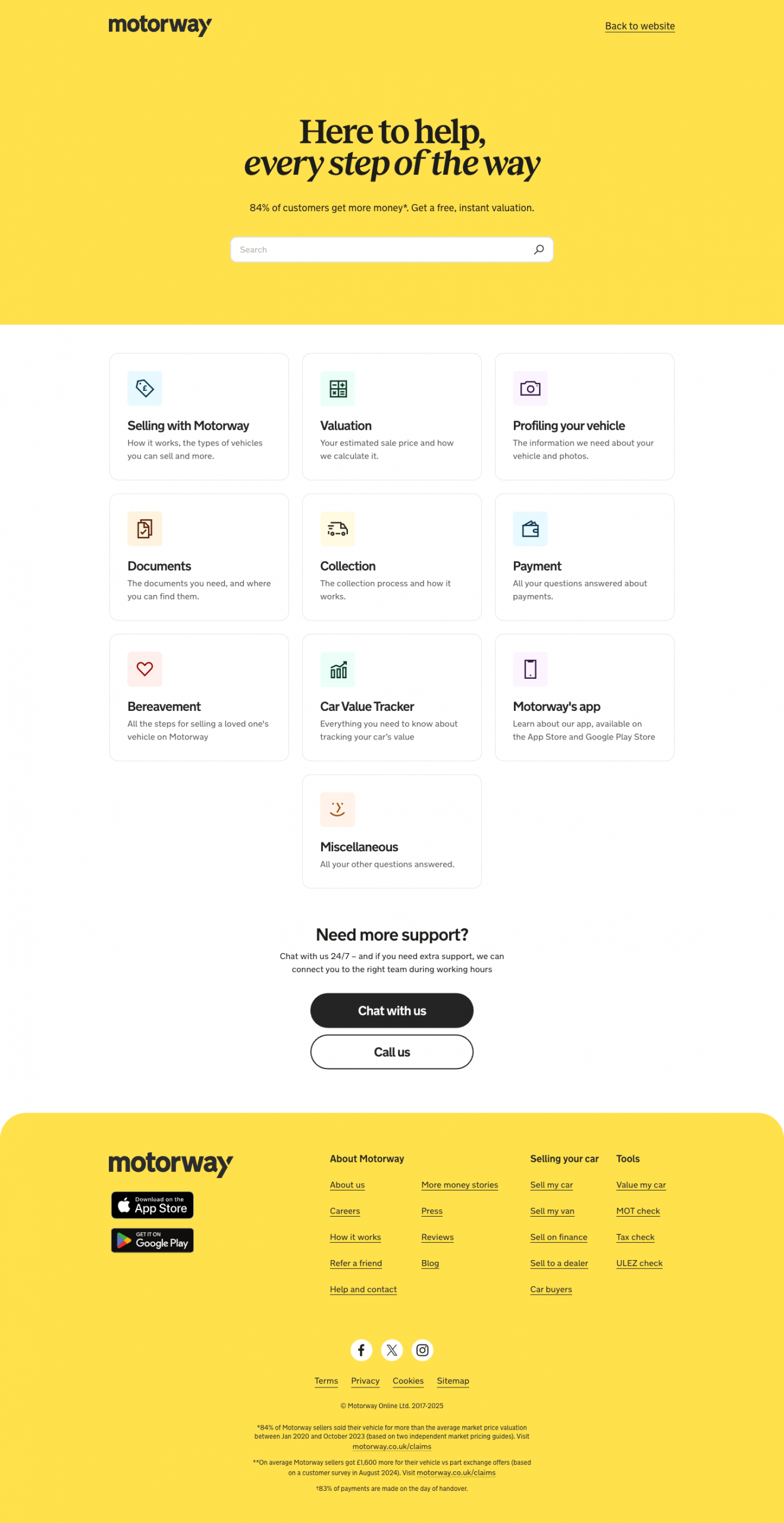
Motorway’s help centre doesn’t just match their main website. It feels like a seamless extension of it. With intuitive navigation and a lightning-fast search, customers can find answers in seconds. Here are some standout Zendesk help centre customisations Motorway has put in place:
- The visually appealing mix of text and icons ensures a smooth reading experience.
- Categories like ‘Selling with Motorway’ and ‘Valuation’, are packed with concise guides and FAQs to equip users with all relevant information.
- Need more help? The standout contact info and 24/7 support options are ready to assist.
- Handy footer links guide you to more resources effortlessly.
Structure and Article Strategy
A well-organised self-service knowledge base is a Zendesk best practice that can dramatically reduce ticket volume and boost customer satisfaction.
How to do it:
- Categories and sections: Group articles by themes (e.g., “Account Management,” “Payments,” “Technical Issues”).
- Featured articles: Feature the most-accessed or critical articles on the Help Centre homepage.
- Search analytics: Use Zendesk’s analytics to see what customers are searching for and spot missing answers.
Example:
A fintech company noticed lots of “troubleshooting deposit” searches. They created a new article, prominently featured it, and reduced related tickets by 40%.
Article Writing and Maintenance
Zendesk best practices mean your knowledge base is never “set and forget.” Keep it clear, helpful, and up-to-date.
How to do it:
- Simple language: Write as if you’re explaining to a friend.
- Step-by-step instructions: Break down tasks into clear steps.
- Screenshots and visuals: Use images, GIFs, or even short videos for complex tasks.
- FAQs: Add a section for common follow-up questions.
- Ownership: Assign each article to a team member for regular review.
Example:
A SaaS company’s “Getting Started” guide is reviewed quarterly by the product manager, who updates it after every major release.
4. Customer Communication
Multichannel Support
Zendesk best practices recommend being present where your customers are: email, chat, social media, or phone.
How to do it:
- Integrate all channels: Bring email, chat, social, and phone into Zendesk.
- Channel-specific workflows: Route tickets from each channel to the right team or queue.
- Channel-specific SLAs: Chat and social may need faster replies than email.
Example:
Customers reached out to a retailer through every platform imaginable: email, phone, social media, and chat. To meet them wherever they were, the company boosted its presence on all these channels:
- Email and phone for those who like the classic approach
- Live chat and WhatsApp for instant, mobile-friendly help
- Social media integration to connect with younger, digital-savvy shoppers
At first, delivering a consistent experience everywhere was a real challenge. But with Zendesk’s omnichannel capabilities, the retailer brought all those conversations together in a single interface.
Now, agents can handle every customer question, no matter where it comes from, from a single place and always see the customer’s full history. Nothing gets missed, and every customer gets the seamless support they expect.
Emilie Serra, CX Manager at JULES
Automation and CSAT
Automating notifications and CSAT surveys is a Zendesk best practice for measuring and improving your service quality.
How to do it:
- Automate CSAT surveys after each solved ticket.
- Set up triggers for follow-up on low scores.
- Review feedback regularly and use it for coaching and improvements.
Example:
A tech company reviews CSAT feedback weekly, identifying and fixing recurring issues, such as confusing instructions or slow replies.
5. Analytics, Reporting, and Continuous Improvement
Dashboards and Metrics
Zendesk best practices are built on data. Use dashboards and regular reports to spot trends, solve problems, and celebrate wins.
How to do it:
- Use Zendesk Explore: Track first reply time, resolution time, ticket volume, and CSAT.
- Share dashboards: Make data visible to everyone. Transparency drives improvement.
- Act on insights: Adjust staffing, workflows, or FAQs based on what you see in the numbers.
Example:
YOTEL, an international hotel brand, took their operations to the next level by rolling out advanced reporting. They have custom-built Zendesk reports tracking every activity across their hotels.
With these powerful analytics, the team gets instant clarity on what’s working and what needs attention. Now, they can quickly spot areas for optimisation, prioritise changes, and keep raising the bar for guest experience, ensuring Zendesk’s continuous improvement is part of their daily routine.
“We got off the ground in two weeks. It’s the fastest I’ve seen, and we started seeing results instantly. The responsiveness of our team improved immediately. Since implementing Zendesk, we’ve had almost zero complaints because inquiries are directed to the right team and are addressed quickly.”
Benchmarking
Comparing your team’s numbers to industry standards is a Zendesk best practice for setting realistic, motivating goals.
How to do it:
- Use Zendesk Benchmark to compare response times, satisfaction, and other key metrics.
- Set targeted improvements based on where you stand.
Example:
A B2B support team found their first reply time was above the industry average. They hired another agent and refined their workflows, improving their stats in the next quarter.
6. Health Checks, Change Management, and Disaster Recovery
Health Checks
Regular Zendesk health checks are a best practice for keeping things running smoothly and avoiding technical debt.
How to do it:
- Do regular health checks: Follow a free Health Check Guide from Premium Plus or get your instance reviewed by Zendesk experts.
- Remove clutter: Delete old macros, unused integrations, and views.
- Document changes: Log what you update and why.
Example:
A quarterly Zendesk health check uncovered old triggers that slowed down ticket assignments. After the cleanup, the team saw faster response times and a happier support staff.

Download the free Zendesk Health Check Guide and discover proven tips to:
- boost agent productivity
- optimise triggers and automations
- uncover hidden opportunities in your setup
Change Management and Recovery
Change management and disaster recovery are Zendesk best practices that ensure you’re prepared for anything.
How to do it:
- Change log: Record every major system change: who did it, when, and why.
- Regular backups: Export your Zendesk settings after big updates.
- Test your recovery plan: Once a year, run through your rollback plan with the team.
Change Log Template:
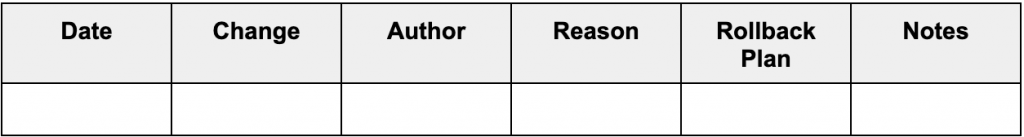
Example:
After a major workflow change, a support team’s careful logging lets them quickly restore the old setup when a new bug appears.
7. Integrations, AI, and Continuous Improvement
Integrations and Automation
Connecting Zendesk to your other business tools is a Zendesk best practice for boosting productivity and scaling effortlessly.
How to do it:
- Integrate with Jira, Salesforce, Slack, or HubSpot: Automate cross-team tasks and keep sales, support, and engineering in sync.
- Use triggers for automation: Automatically create Jira issues for bugs or send urgent alerts to Slack.
- Explore the Zendesk Marketplace: Find industry-specific apps to extend Zendesk’s capabilities.
Example:
Edenred, a leader in digital payment solutions, supercharged their customer service by integrating Zendesk with Aircall, a cutting-edge telephony platform. Now, they handle over 20,000 calls each month with ease.
With Aircall, Edenred achieved:
- A smooth switch to remote work: Their entire team transitioned quickly and efficiently without missing a beat.
- Real-time insights: Managers can monitor team performance live, making instant tweaks to keep everything running at its best.
- Smart call routing: Calls are automatically directed to the most skilled agents, so customers get the help they need fast.
- Crystal-clear call quality: Every conversation sounds as good as it would in the office.
Amazingly, it took just two days for Edenred’s agents to get up and running with these new tools. These tools didn’t just match their old office setup but actually made it better. Thanks to the seamless transition, the team continues to deliver outstanding customer care, no matter where they’re working.
Zendesk AI: AI Agents and Copilot
Zendesk AI is one of the most exciting best practices for delivering fast, efficient support at scale.
How to do it:
- Deploy Zendesk AI Agents for routine questions like “Where is my order?” or password resets.
- Let Zendesk Agent Copilot suggest replies, summarise tickets, and recommend articles for your agents.
- Review AI performance regularly and train your agents to use Copilot as their smart assistant.
Example:
BrightLocal increased the automation rate to 46% with Zendesk AI Agents
The support team at BrightLocal was swamped with repetitive queries, often copying and pasting help centre content into tickets. With 70,000 tickets annually and a team of 24, it was clear something needed to change.
BrightLocal chose Zendesk AI Agents for their ability to simplify the process without requiring extensive flow building. The impact is significant. BrightLocal’s AI Agents solve over 40% of tickets.
Continuous Improvement Programme
Best practices are all about evolution. A culture of Zendesk continuous improvement keeps your support operation sharp.
How to do it:
- Regular reviews: Hold monthly or quarterly sessions to discuss analytics and agent feedback.
- Quick wins: Focus on small, impactful changes like a new macro or a better view.
- Share lessons: Celebrate improvements and encourage everyone to suggest new ideas.
Example:
A logistics team’s quarterly “Zendesk Tune-Up” meetings drive workflow optimisations and keep agents engaged and motivated.
8. Training, Empowerment, and Support Culture
Onboarding and Training
Good training is a Zendesk best practice for building a confident, high-performing team.
How to do it:
- Let new hires practice in a Zendesk sandbox.
- Assign mentors for their first month.
- Make Zendesk training part of onboarding.
Checklist:
- Zendesk login and permissions
- Macro and workflow overview
- Practice tickets in the sandbox
- Shadowing a senior agent
- Help Centre review
- Zendesk course completed
Example:
After expert Zendesk training from Premium Plus, customer service teams boost their speed by 15% using Zendesk. With new skills and smarter workflows, they’re helping customers faster than ever.
Onboarding and Training
A positive, support-first culture is a Zendesk best practice that fuels success and satisfaction.
How to do it:
- Recognise top performers and share positive customer feedback.
- Encourage knowledge sharing and teamwork.
- Give agents a voice in improving workflows and processes.
Example:
A SaaS company’s “Support Hero of the Month” award is based on CSAT scores and peer nominations, boosting morale and inspiring excellence.
Conclusion
Zendesk best practices will help you build a support team that is efficient, reliable, and always improving. By following these proven steps, you’ll create an optimised Zendesk instance that delights customers and empowers agents.
Want to optimise your Zendesk
with expert help?